Prepared for: Architects, Urban Planners, and Parking Design Professionals Purpose: To provide a comprehensive evaluation of two-post versus four-post car stackers, focusing on structural design, mechanical systems, parking usability, regional adoption, and return on investment (ROI). This report aims to inform architectural integration and urban planning decisions in multi-modal parking solutions.
Solid Parking
As urban centers face increasing parking space scarcity, vertical parking solutions such as two-post and four-post car stackers have emerged as critical infrastructure components. These mechanical lifts extend parking capacity vertically without significant horizontal expansion, offering architects and planners adaptable options for dense environments. Beyond space optimization, these systems influence building design, operational efficiency, and lifecycle costs.
This report explores these systems through a multi-dimensional lens, incorporating technical research and market insights, to provide professionals with a data-driven foundation for specifying appropriate car stackers tailored to diverse project needs.
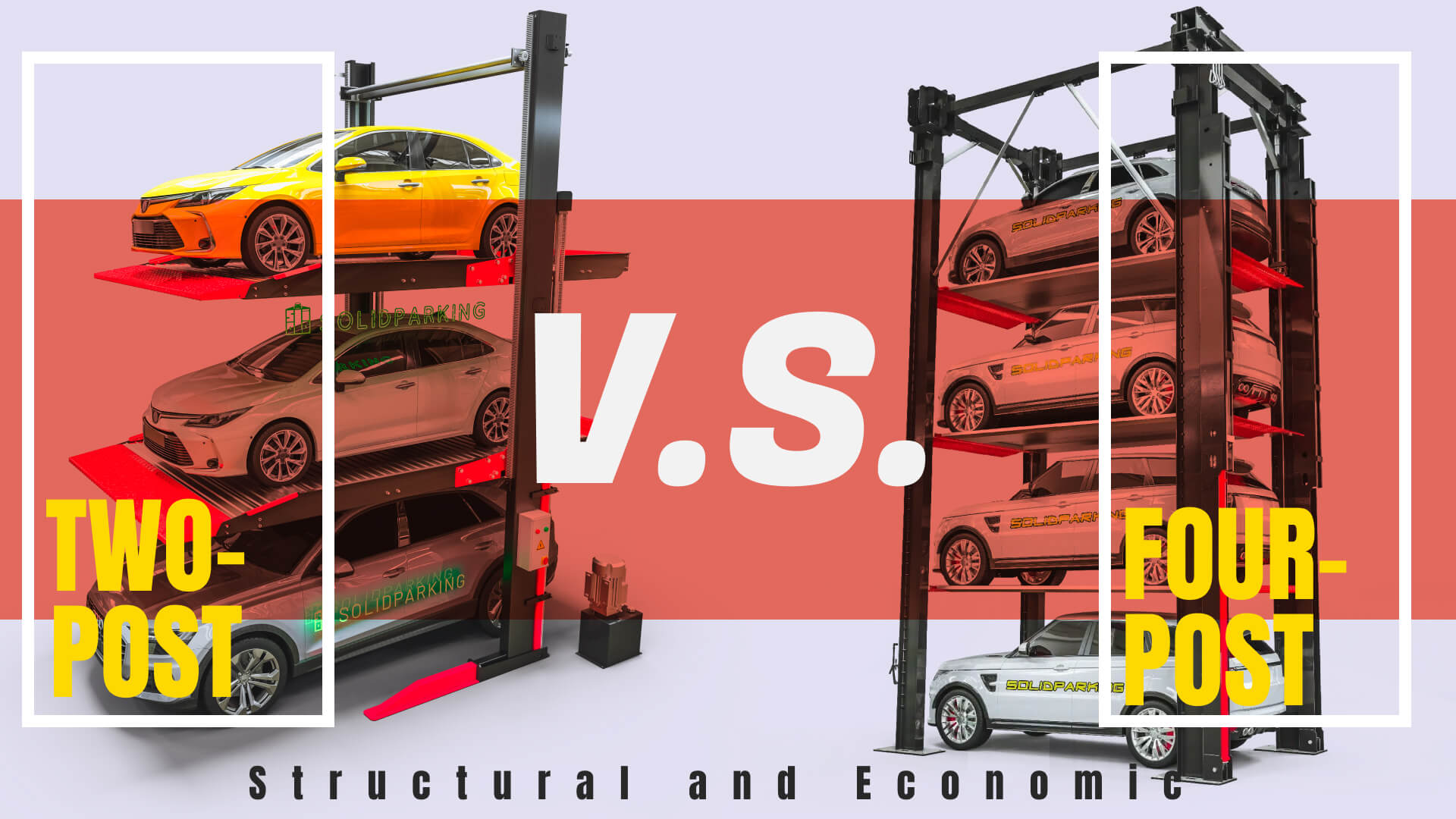
The core difference between two-post and four-post stackers lies in their post configuration and lifting mechanisms, which significantly impact stability, load capacity, and installation requirements.
Feature | Two-Post Car Stacker | Four-Post Car Stacker |
Lifting Mechanism | Hydraulic Cylinder with Chain Drive | Hydraulic Cylinder with Steel Wire Rope |
Number of Posts | 2 Vertical Posts | 4 Vertical Posts |
Platform Support | Suspended (embossed metal plate) | Wheel-supported Runway Plates |
Load Capacity | 2000–3200 kg | 3000–5000 kg |
Installation Precision | High — requires exact post alignment | More tolerant due to four-point support |
Maintenance Needs | Regular lubrication and tension adjustment of chains | Periodic inspection of steel wire ropes |
Two-post stackers utilize hydraulic cylinders paired with chains to raise the platform, requiring precise installation to maintain balance and safety. Their suspended platform design, often featuring embossed galvanized steel plates, optimizes space but demands more attentive maintenance. Four-post stackers, by contrast, employ steel wire ropes, which provide elasticity and enhanced load distribution across four vertical posts and a runway platform supporting vehicle wheels. This configuration offers greater lateral stability, accommodating heavier vehicles and frequent use in commercial environments.
Platform surface design impacts vehicle safety, operational functionality, and environmental durability.
Feature | Two-Post Platform: Embossed Plate | Four-Post Platform: Runway Plate |
Material | Hot-dip galvanized embossed steel | Perforated steel runways with central drip tray |
Surface Texture | Raised embossed patterns for anti-slip | Patterned with open cavities for drainage |
Accessory Integration | Moderate – compatible with some jacks | High – accommodates oil drip trays and hydraulic jacks |
Outdoor Suitability | Excellent with hot-dip galvanization | Good with epoxy zinc coating; iron drip trays available |

Two-post platforms, typically called embossed plates, feature raised patterns created by a cold embossing process. This design enhances tire grip and safety, especially important for wet or slippery surfaces. Historically, corrugated (“waving”) steel plates were used but have largely been replaced due to durability and slip-resistance considerations. Four-post platforms use perforated runway plates with a hollow center that allows for drainage and placement of service equipment such as oil drip trays or hydraulic jacks, making them preferable in automotive service environments. The use of hot-dip galvanization for two-post systems enhances corrosion resistance, particularly critical for outdoor installations.
Both stacker types incorporate multi-layered safety features to comply with international standards.
Safety Feature | Two-Post Stackers | Four-Post Stackers |
Dual Safety Locking | Mechanical & Hydraulic | Mechanical & Hydraulic |
Emergency Stop Mechanism | Yes | Yes |
Overload Protection | Yes | Yes |
Lock Release | Standard | Optional |
Remote Control | Optional | Optional |
Safety is paramount, especially in automated or semi-automated parking systems. Both two-post and four-post car stackers are designed to meet ANSI/ALI ALCTV and ISO mechanical lift safety standards, incorporating dual mechanical and hydraulic locking systems to prevent accidental descent. Emergency stops and overload protections further safeguard users.
User interface and parking ergonomics differ notably between two-post and four-post stackers.
Aspect | Two-Post System | Four-Post System |
Vehicle Access | Unobstructed front access | Posts at vehicle sides may obstruct |
Parking Maneuvering | Easier, better visibility | Slightly more complex due to posts |
Noise & Vibration | Moderate noise from chains | Generally quieter operation |
Suitability for Outdoor Use | Superior with hot-dip galvanized coating | Good with epoxy coatings |
Two-post systems offer an unobstructed driving path as the vehicle is lifted by side arms, improving the driver’s approach and reducing the risk of collision with structural elements. However, this design requires careful spatial planning. Four-post lifts support vehicles on runways that allow easy parking but include four vertical posts that can slightly hinder maneuverability, especially in tight spaces. Noise considerations and durability factors also guide selection based on indoor versus outdoor use.
Region | Preferred Stackers | Typical Applications |
North America | Four-Post | Automotive repair shops, storage facilities |
Europe | Two-Post | Urban parking, valet systems |
Southeast Asia | Two-Post | Residential complexes, compact lots |
Middle East | Both | Luxury parking, mixed-use developments |
Australia/New Zealand | Four-Post | Home garages, commercial parking |
China & Korea | Mixed | Service centers (4-post), residential (2-post) |
Regional preferences reflect urban density, vehicle fleet characteristics, and economic priorities. North American markets favor four-post lifts due to their suitability for heavy-duty use and service integration. European and Asian urban environments prioritize two-post lifts for space efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The Middle East integrates both types based on luxury and service needs. This global diversity necessitates tailored architectural specifications considering local market trends.
Parameter | Two-Post Car Stackers | Four-Post Car Stackers |
Initial Investment | Optimized cantilevered design and chain-driven mechanics deliver high performance at a cost-effective price point. | Lower upfront cost due to simpler structure and installation |
Operational Efficiency | High space utilization | Enhanced service revenue potential |
Maintenance Costs | Moderate (chain tension, lubrication) | Moderate to high (wire ropes inspection) |
Typical Payback Period | 6–18 months | 12–36 months |
Revenue Streams | Increased parking capacity | Parking + service facility income |
Two-post stackers often offer high space efficiency and are favored for their compact design, especially in projects focused on valet, residential, or mixed-use parking. However, four-post stackers typically come at a lower initial cost and simpler installation, making them a more economical choice for many businesses—particularly automotive service providers and residential garages. Their ability to double as both parking and maintenance platforms adds functional value. ROI ultimately depends on the intended use case, maintenance environment, and revenue strategy. Choosing the right system aligned with long-term operational goals is key to maximizing investment returns.
Understanding the distinctions between two-post and four-post car stackers becomes far more intuitive when seen in real-life context. The following gallery offers a glimpse into how these systems are integrated across diverse architectural and operational environments—transforming parking challenges into streamlined, efficient solutions.
Two-post and four-post car stackers each present unique advantages in addressing modern parking challenges. Two-post systems excel in compactness, cost efficiency, and ease of installation, fitting urban residential and valet applications. Four-post lifts provide superior load capacity, operational versatility, and enhanced user safety, aligning well with commercial, industrial, and service-oriented parking demands.
Architectural professionals should evaluate these technologies through the lenses of site constraints, user experience, maintenance capabilities, and financial models. Integrated thoughtfully, both stacker types contribute to sustainable, space-conscious urban mobility frameworks and deliver measurable economic benefits.
